Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (16): 2480-2486.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.16.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of fluoride release and solubility for different glass ionomer cements
Liu Li-xia1, Chen Lin2
- 1Department of Stomatology, Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen City, Shenzhen 518035, Guangdong Province, China; 2Jinjue Dental Institute, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Revised:2014-02-22Online:2014-04-16Published:2014-04-16 -
Contact:Chen Lin, Jinjue Dental Institute, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Liu Li-xia, Attending physician, Department of Stomatology, Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen City, Shenzhen 518035, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Li-xia, Chen Lin. Comparison of fluoride release and solubility for different glass ionomer cements[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2480-2486.
share this article
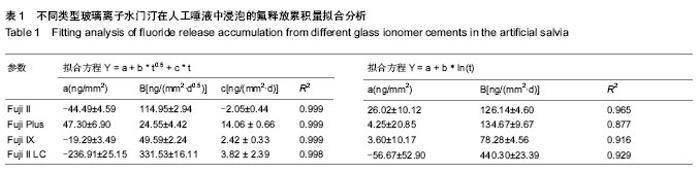
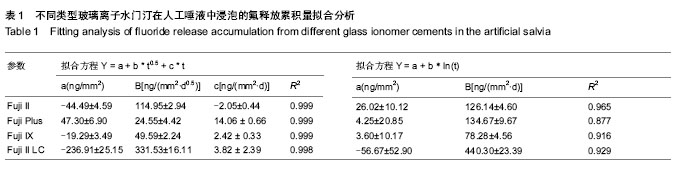
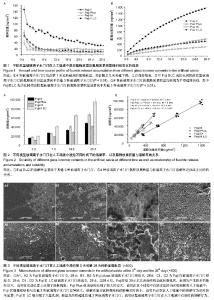
2.1 不同类型玻璃离子水门汀氟释放量的动态变化趋势 将不同类型玻璃离子水门汀试样放入人工唾液中后,采用氟离子选择电极检测每天玻璃离子水门汀试样的氟释放量,结果见图1A所示。对照组与3种改性玻璃离子水门汀均在第1天达到最高的氟释放量,而在随后几天迅速下降,实验进行7 d后,Fuji Ⅱ(对照组),Fuji Plus和Fuji Ⅸ的氟释放量保持稳定,数值分别为9.28-16.81 ng/mm2,14.38-18.97 ng/mm2和6.34-12.78 ng/mm2,而Fuji Ⅱ LC的氟释放量保持缓速下降的趋势,从第8天的68.16 ng/mm2逐渐下降到第28天的28.99 ng/mm2。对4种玻璃离子水门汀的平行比较中,Fuji Ⅱ LC与其他3组的组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),可认为Fuji Ⅱ LC表现出显著高于其他3种玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放量,而其他3种玻璃离子水门汀组间的氟释放量差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),说明这3种玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放行为较为类似。 2.2 不同类型玻璃离子水门汀氟释放累积量的动态变化趋势 图1B显示不同类型玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放累积量随时间变化趋势,如图可知对照组和3种改性玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放累积量随时间变化趋势均表现为平滑递增曲线,说明对照组与改性玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放行为均较为稳定。4种玻璃离子水门汀中,FujiⅡLC仍表现出显著高于其他3种玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放累积量(P < 0.01),在第28天时达到1 598.3 ng/mm2。FujiⅡ和Fuji Plus 的氟释放累积量变化趋势较为类似,在第28天时分别达到497.3 ng/mm2和570.0 ng/mm2。Fuji Ⅸ的氟释放累积量相对最低,为307.6 ng/mm2。 2.3 不同类型玻璃离子水门汀氟释放累积量的拟合分析 采用两种拟合方程 Y=a+b * t0.5 +c * t 和 Y=a+b * ln(t)对对照组和3种改性玻璃离子水门汀氟释放累积量进行非线性回归分析。表1分别显示这两种方程的重要参数数值和相关系数R2。如表可知,方程Y=a+b * t0.5 +c * t 可以较好模拟各种类型玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放过程,对Fuji Ⅱ、Fuji Plus和Fuji Ⅸ的相关系数均为0.999,Fuji Ⅱ LC也达到了0.998;相反,方程Y=a+b * ln(t) 的模拟结果相对较差,难以真实反映这4种玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放行为,对对照组的拟合相关系数只有0.965,对Fuji Plus、FujiⅨ和FujiⅡ LC相关系数甚至更低,分别为0.877,0.916和0.929。"
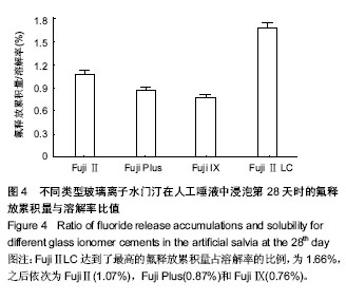
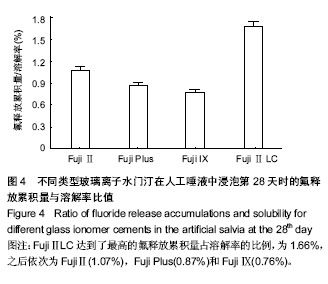
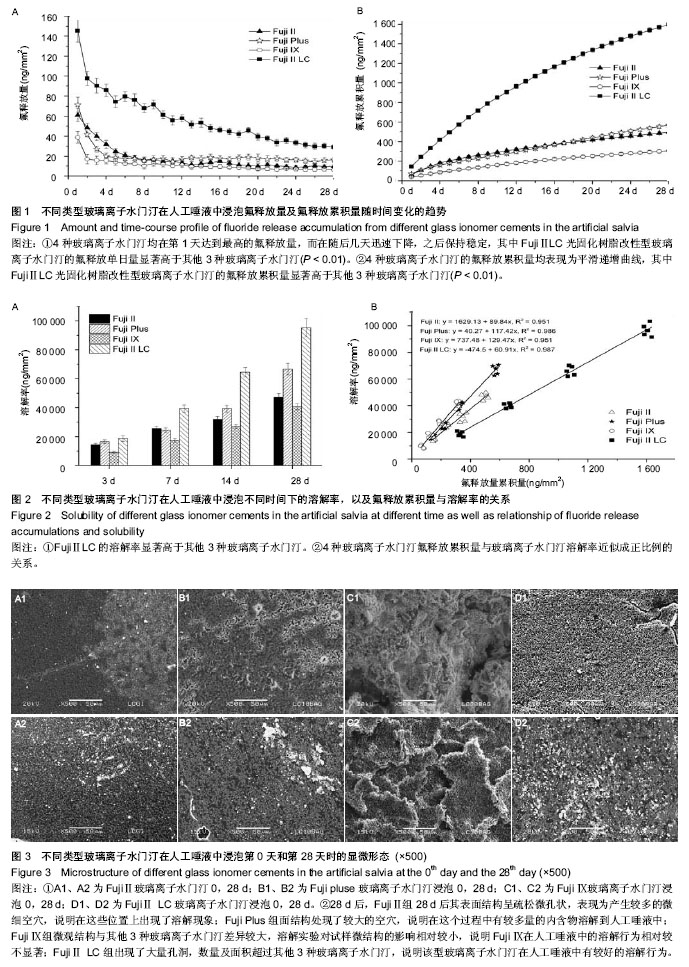
2.4 不同类型玻璃离子水门汀在不同时间下的溶解率 图2A显示对照组和3种改性玻璃离子水门汀在第3,7,14,28天时的溶解率,如图可知,Fuji Ⅱ LC的溶解率显著高于其他3种玻璃离子水门汀,其次为Fuji Plus。FujiⅡ和Fuji Ⅸ的溶解率相差不大。在第28天时,Fuji Ⅱ LC的溶解率达到95 278 ng/mm2,之后为Fuji Plus(66 603 ng/mm2),最后为Fuji Ⅱ(47 296 ng/mm2)和Fuji Ⅸ(40 670 ng/mm2)。 2.5 不同类型玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放累积量与容积率的关系 图2B显示对照组和3种改性玻璃离子水门汀氟释放累积量与容积率的关系,可以看出对4种玻璃离子水门汀,氟释放累积量与玻璃离子水门汀溶解率近似成正比例的关系,对Fuji Ⅱ和Fuji Ⅸ,相关系数为0.951,对Fuji Plus和Fuji Ⅱ LC,相关系数更达到0.986和0.987。对4种玻璃离子水门汀来说,溶解率越高氟释放累积量越大,氟释放累积量随溶解率升高而变大。 2.6 不同类型玻璃离子水门汀在第0天和第28天的微观结构 图3显示各玻璃离子水门汀在第0天和第28天通过扫描电镜得到的微观结构图。如图可知,对照组在放入人工唾液28 d后,其表面结构呈疏松微孔状,表现为产生较多的微细空穴,说明在这些位置上出现了溶解现象。对Fuji Plus,可以看出溶解实验后试样的表面结构处现了较大的空穴,说明在这个过程中有较多量的内含物溶解到人工唾液中。对Fuji Ⅸ,其微观结构与其他3种玻璃离子水门汀差异较大,溶解实验对试样微结构的影响相对较小,说明Fuji Ⅸ在人工唾液中的溶解行为相对较不显著。对Fuji Ⅱ LC,其在溶解实验后出现了大量孔洞,数量及面积超过其他3种玻璃离子水门汀,说明该型玻璃离子水门汀在人工唾液中具有较好的溶解行为。 2.7 各种玻璃离子水门汀氟释放累积量与溶解率的比值 图4显示4种玻璃离子水门汀在第28天时的氟释放累积量与溶解率的比值。如图可知,Fuji Ⅱ LC达到了最高的氟释放累积量占溶解率的比例,为1.66%,之后依次为 Fuji Ⅱ (1.07%),Fuji Plus(0.87%)和Fuji Ⅸ(0.76%)。"
| [1] 王瑾,程为庄.玻璃离子水门汀的研究进展[J].北京生物医学工程, 2005,24(2):139-143. [2] Leinfelder KF. Glass Ionomer: current clinical development. J Am Dent Assoc. 1993;124(9):62-64. [3] Forsten L.Resin-modified glass-ionomer cements fluoride release and uptake. Acta Odonto Scand.1995;53:222-225. [4] Wilson AD,Kent BE.The glass-ionomer cement. A new translucent dental filling material.Appl Chem Biotechnol.1971;21:313-320. [5] Smith DC.Glass ionomer cements:a prospect, In:Proceedings of the Symposium on Aesthetic Restorative Materials.J Am Dent Assoc.1993:49-59. [6] Zhang L,Wang X,Liu HY.Bond strength between titanium alloy with different surface roughness and dentin.J Clin Rehab.2009; 13(49):9398-9400. [7] Balamungan A,Baiossier G,Lanrent-Maquifi D,et al.An in vitro biological and antibacterial study oll a sollel derived silver-incerporated biogless system. Dent Mater. 2008;24(10): 1343-1351. [8] Lucas ME,Arita K,Nishino M.Strengthening a conventional glass ionomer cement using hydroxyapatit.J Dent Res.2001;80 (special issue):711. [9] Lohbauera U,Walker J,Nikolaenko S,et al.Reactive fibre reinforced glass ionomer ecements.Biomaterials. 2003;24(17): 2901-2907. [10] 崔恺,陈吉华,赵三军.玻璃离子水门汀的研究进展[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志. 2008,18(11):644-647. [11] Arita K,Lucas ME,Nishino M.The effect of adding hydroxyapatite on the flexural strength of glass ionomer cement.Dent Mater. 2003; 22(2):126-136. [12] Lucas ME,Arita K,Nishino M.Flexural strength of hydroxyapatite- added glass ionomer cement.J Dent Res. 2002; 81(Special issue A):36. [13] Gu YW,Yap AUJ,Cheang P,et al.Zirconia-glass ionomer cement potential substitute for Mieade Mix.Biomaterials. 2004;52(2): 113-116. [14] Smith DC.Glass ionomer cements.In: Kawahra H, editor, Proceedings of the International Congress on Implant Bio-mater in Stomata.Tokyo: Ishiyaku, 1980:26-54. [15] Smith DC.A review of the zinc polycarboxylate cements.J Can Dent Ass. 1971;37:22-30. [16] Wilson AD,Crisp S,Abel G.Characterization of glass-ionomer cements: Effect of molecular weight on physical properties.J Dent.1977;5:117-120. [17] Prosser HJ,Powis DR,Wilson AD.Glass-ionomer cements of improved flexural strength.J Dent Res.1986;65:146-148. [18] Nakajima N,Watkins JH,Arita K,et al. Mechanical properties of glass ionomers under static and dynamic loading.Dent Mater. 1996;12:30-37. [19] Helena YU,Liptxo VJLT,Timo N,et al.Compressive strength and surface characterization of glas ionomer cements modified by particle of bioactive glass. Dent Mater.2005;21(3):201-209. [20] Yli-Urpo H,Vallittu PK, Närhi TO,et al.Release of silica, calcium, phosphorus and fluoride fromglass ionomer cernent containing bioactive glass.J Biomater Appl.2004;19(1):5-20. [21] Nychka JA,Li D,Alexander B.In vitro bioactivity of 45S5 bioactive glass as a function of indentation load.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2008;1(3):243-251. [22] Marending M,Stark WJ,Brunner TJ,et al.Comparative assessment of time-related bioactive glass and calcium hydroxide effects on mechanical properties of human root dentin. Dent Traumatol.2009;25(1):126-129. [23] Choi JY,Lee HH,Kim HW.Bioactive sol-gel glass added ionomer cement for the regeneration of tooth structure.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2008;19(10):3287-3294. [24] Xie D,Zhao J,Weng Y,et al.Bioactive glass-ionomer cement with potential therapeutic function to dentip capping mineralization.J Oral Sci.2008;116(5):479-487. [25] Zehnder M,Sôdealing E,Sahnen J,et al. Preliminary evaluation of bioactive glass S53P4 as an endedontic medication in vitro. J Endod.2004;30(4);220-224. [26] Lohbauera U,Walker J,Nikolaenko S,et al.Reactive fibre reinforced glass ionomer ecements. Biomaterials. 2003;24(17): 2901-2907. [27] Masayuki KAGA,Masahiro K,Kosuke I,et al.Cytotoxicity of Strengthened Glass-ionomer Cement by Compounding Short Fibers with CaO-P2O5-SiO2-Al2O3 Glass. Nano Biomed. 2010;2(1):23-30. [28] MeCabe JF. Resin-modified glass-ionomers. Biomaterials. 1998; 19(6):521-527. [29] 曹院琴,李永祥.3种玻璃离子水门汀氟释放能力的体外研究[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2013,11(2):116-118. [30] Mousavinasab MS,Meyers I.Fluoride release and uptake by glass ionomer cements. compomers and giomers.Res J Biol Sci.2009;4(5):609- 616. [31] Chan WD,Yang L,Wang W,et al. Fluoride release from dental cements and composites: a mechanistic study.Dent Mater. 2006;22(4):366- 373. [32] Verbeeck RM,deMoor RJ,Van Even DF,et al.The short-term fluoride release of a hand - mixed vs. cap sulated system of a restorative glass - ionomer cement. J Dent Res. 1993;72: 577-581. [33] Musa A,Pearson GL,Gelbier M.In vitro investigation of fluoride ion release from four resin - modified glass polyalkenoate cements. Biomaterials.1996;17(10): 1019-1023. [34] 张军,彭彬.不同类型玻璃离子水门汀氟离子体外释放的比较[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2008,18(1):28-30. [35] Williams JA,Billington RW,Pearson GJ. A long term study of fluoride release from metal - containing conventional and resin- modified glass-ionomer cements. J Oral Rehabil. 2001;28(1): 41-47. [36] 赵守亮,宋江红,王景杰,等.玻璃离子水门汀加入银合金粉后对其抗压强度和表面硬度的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 1997,7(4): 246-247. [37] Moreau JL,Xu HH.Fluoride releasing restorative materials: Effects of pH on mechanical properties and ion release.Dent Mater.2010;26(11):e227-e235. [38] Kuhn AT,Wilson AD.The dissolution mechanisms of silicate and glass-ionomer dental cements.Biomaterials.1985;6(6):378-382. [39] 厚继续,张彩霞,陈德敏,等.玻璃离子水门汀释放氟实验研究[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2002,11(4):175-183. [40] 韩宁宁,莫三心.不同pH 值的浸泡液对玻璃离子水门汀溶解性的影响[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2007,16(1):15-17. [41] 吴玮,陈吉华,赵三军.3种水门汀早期溶解性比较研究[J].口腔医学研究,2007,23(2):194-196. [42] Tllrklln LS,Turkan M,Ertugrul,et al.Long-term antibacterial effects and physical properties of a chlorhexidine-containing glass ionomer cement. J Esthet Restor Dent.2008;20(1):29-45. [43] Kawano F,Kon M,Kobayashi M,et al.Reinforcement effect of short glass fibers with CaO-P2O5-SiO2-Al2O3 Glass on strength of glass ionomer elements.J Dent. 2001;29(5):377-380. [44] 程汉亭,刘韩星,肖群.玻璃离子水门汀短期力学性能的研究[J].生物医学工程研究, 2005,24(1):55-57. [45] Zimehl R,Hannig M.Non metaIlic restorative materials based on glass ionomer cements-recent trends and developments. Colloids and Surfaces.2000;63:55-55. [46] 张海英,侯本祥,陈薇.四种玻璃离子充填材料释氟性与溶解性的研究[J].北京口腔医学, 2011,19(5):260-262. [47] 崔恺,陈吉华,赵三军.不同剂型玻璃离子水门汀溶解性比较研究[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2008,18(2):87-89. |
| [1] | Song Hua, Ren Xiang-qian, Wei Dong-xing. Nano-hydroxyapatite effects on bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1155-1159. |
| [2] | Xue Zhen, Niu Li-yuan, An Gang, Guo Ya-shan, Lv Song-cen. Feasibility of nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan/calcium sulphate hemihydrate as an injectable bone tissue engineering scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1160-1164. |
| [3] | He Yan-ping, Ma De-chun, Li Lei, Zhang Li, Zheng Shuang, Dong Ke-xin. Hemocompatibility and surface modification of artificial blood vessel materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1272-1276. |
| [4] | Li Bing-ting, Jia Ying-zhen, Liu Zhi-fang, Song Yuan, Hou Xiao-wei. Effect of freeze-dried bone xenograft and platelet-rich fibrin compound on osteogenesis and osseointegration of alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8376-8381. |
| [5] | Wu Tao, Wu Jin-hui, Zheng Guo-dong, Lu Zhi-qin, Zeng Hai-yan, Lv Jun, Xing Jian-zhou. Release behavior of icariin-chitosan/hydroxyapatite scaffolds in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8399-8404. |
| [6] | Wang Xiao-dong, Zhang Yong-hong. Preparation and performance of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2-poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyoctanoate) nanospheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8405-8408. |
| [7] | Fan Ke-xia, Ma Yuan2, Yu Si-xun, Kuang Yong-qin, Yang Li-bin, Xia Xun, Zhao You-guang, Yang Wei-zhong, Gu Jian-wen. Preparation and in vitro biocompatibility of hydroxyapatite/polyphenylene sulfide composites [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8443-8449. |
| [8] | Feng Chao, Li Zhe, Lv Xiang-guo, Xu Yue-min, Fu Qiang. In vitro preparation and biochemical evaluation of oxygen generative keratin/silk fibroin compound biomaterial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8480-8486. |
| [9] | Li Tian-shi, Zeng Wen-ni, He Jun-jun. Chitin and its derivatives inhibit scar formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8504-8508. |
| [10] | Ma Song-feng, Cao Hui, Zheng Feng, Qiao Jun, Zhang Guo-ming. Concomitant cardiac valve replacement and coronary artery bypass grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 699-704. |
| [11] | Kang Wen, Xu Guo-qiang, Diilnur Aji, Wei Qng, Ma Hui, Li Zhao-peng, Song Qian, Rufiya Zulati, Alina Abdujilil, Pahirdin Kaisar. In vitro cytotoxicity of the hydroxyapatite/barium titanate biological piezoelectric ceramic coating [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5466-5472. |
| [12] | Lu Hua-ding, Lian Li-yi, Chen Ming-wei, Dai Yu-hu. Cloning and expression of Asperguillus endo-chitosanase gene in Escherichia coli [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5490-5496. |
| [13] | Fan Zhong-bao, Rong Da-qing, Liu Qing-feng. Prolene hernia system versus polypropylene mesh plug in tension-free hernia repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5535-5539. |
| [14] | Li A-li. Absorbable ligating clip in laparoscopic hysterectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5561-5565. |
| [15] | Huang Xiao-nan. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: high-viscosity versus low-viscosity bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2461-2467. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||